Refraction at Plane and Spherical Surfaces
Refraction at Plane and Spherical Surfaces: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Refraction of Light, Absolute Refractive Index, Vertical Shift Due to Glass Slab & Refractive Index of a Glass Slab using a Travelling Microscope etc.
Important Questions on Refraction at Plane and Spherical Surfaces
The reason for using lead glass in the preparation of lenses is ,it is
When a monochromatic light ray is incident on a medium of refractive index with an angle of incidence , the angle of refraction is . If is changed slightly by , then the corresponding change in will be
A spherical thick shell made of transparent material is cut along its chord as shown. The smaller part will
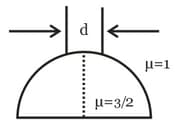
A beam of diameter 'd' is incident on a glass hemisphere as shown. If the radius of curvature of the hemisphere is very large in comparison to d, then the diameter of the beam at the base of the hemisphere will be
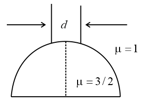
A beam of diameter is incident on a glass hemisphere as shown. If the radius of curvature of the hemisphere is very large in comparison to , then the diameter of the beam at the base of the hemisphere will be
A concave spherical surface of radius of curvature 10 cm separates two medium x & y 0f refractive index 4/3 & 3/2 respectively. If the object is placed along principal axis in medium X then
A ray of light moving along the unit vector undergoes refraction at an interface of two media, which is the plane. The refractive index for is while for , it is . The unit vector along which the refracted ray moves is
A parallel sided block of glass of refractive index which is thick rests on the floor of a tank which is filled with water (refractive index). The difference between the apparent depth of floor at and when seen from vertically above is equal to
A bird is flying 3 m above the surface of water. If the bird is diving vertically down with speed = 6 m/s, his apparent velocity as seen by a stationary fish underwater is:
A ray of sunlight enters a spherical water droplet () at an angle of incidence measured with respect to the normal to the surface. It is reflected from the back surface of the droplet and re-enters into the air. The angle between the incoming and outgoing ray is [Take ]
A surveyor on one bank of canal observed the image of the 4 inch and 17 ft marks on a vertical staff, which is partially immersed in the water and held against the bank directly opposite to him, coincides. If the 17 ft mark and the surveyor's eye are both 6 ft above the water level, If the width of the canal is 10 + x, assuming that the refractive index of the water is 4/3, then find the value of x. Zero mark is at the bottom of the canal.
A surveyor on one bank of canal observed the image of the 4 inch and 17 ft marks on a vertical staff, which is partially immersed in the water and held against the bank directly opposite to him, coincides. If the 17 ft mark and the surveyor's eye are both 6 ft above the water level, If the width of the canal is 10 + x, assuming that the refractive index of the water is 4/3, then find the value of x. Zero mark is at the bottom of the canal.
A narrow parallel beam of light is incident on a transparent sphere of refractive index . If the beam finally gets focussed at a point situated at a distance = 2 × (radius of sphere) from the centre of the sphere, then find ?
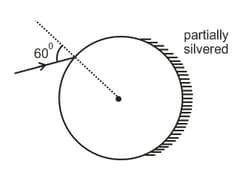
A ray is incident on a glass sphere as shown. The opposite surface of the sphere is partially silvered. If the net deviation of the ray transmitted at the partially silvered surface is 1/3rd of the net deviation suffered by the ray reflected at the partially silvered surface (after emerging out of the sphere). Find the refractive index of the sphere.
A point object is placed at a distance of from a convex lens of focal length . If a glass slab of thickness and refractive index is inserted between the lens and object. The image is formed at infinity. Find the thickness .
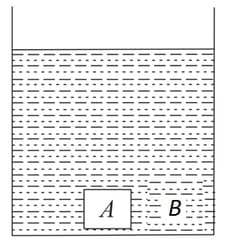
A beam of parallel rays of width b propagates in glass at over to air this face is _________ if the refractive index of glass is μ.v
When light travels from a rarer to a denser medium, which of the following parameter of light decreases:
A thin lens of refractive index has a focal length of in air. When the lens is placed in a medium of refractive index its focal length will become _________ .
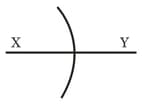
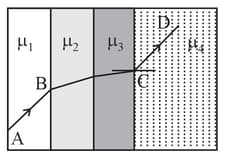
A ray of light passes through four transparent media with refractive indices and as shown in the figure. The surfaces of all media are parallel. If the emergent ray is parallel to the incident ray , we must have
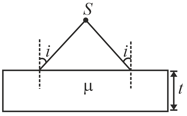
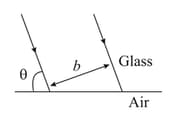
A diverging beam of light from a point source S having divergence angle , falls symmetrically on a glass slab as shown. The angles of incidence of the two extreme rays are equal. If the thickness of the glass slab is t and the refractive index n, then the divergence angle of the emergent beam is